No disponible.
Artículo vendido en nuestra tienda (2023)
Precio : 60.00 €
Artículo vendido en nuestra tienda (2023)
Precio : 60.00 €
Tipo : Médaille, Albert Einstein
Fecha: 1955
Metal: bronce
Diámetro: 59,5 mm
Eje de acuñación: 12 h.
Acuñador Fonderie Huguenin, Chaux de Fonds
Peso: 99,15 g.
Canto: lisse
Cuño: sans poinçon
Comentarios sobre el estado de conservación:
Patine hétérogène avec des taches noires et des concrétions vertes, notamment au revers
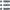
Anverso
Titulatura del anverso: ALBERT / EINSTEIN / 1879-1955.
Descripción del anverso: Buste de profil à droite, signé : R. HUGUENIN.
Reverso
Titulatura del reverso: LISSE.
Comentario
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) est un physicien théoricien. Il publie sa théorie de la relativité restreinte en 1905 et sa théorie de la gravitation, dite relativité générale, en 1915. Il contribue largement au développement de la mécanique quantique et de la cosmologie, et reçoit le prix Nobel de physique de 1921 pour son explication de l’effet photoélectrique. Son travail est notamment connu du grand public pour l’équation E=mc², qui établit une équivalence entre la masse et l’énergie d’un système..
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) was a theoretical physicist. He published his theory of special relativity in 1905 and his theory of gravitation, known as general relativity, in 1915. He contributed significantly to the development of quantum mechanics and cosmology, and received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. His work is particularly well known to the general public for the equation E=mc², which establishes an equivalence between the mass and energy of a system.
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) was a theoretical physicist. He published his theory of special relativity in 1905 and his theory of gravitation, known as general relativity, in 1915. He contributed significantly to the development of quantum mechanics and cosmology, and received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. His work is particularly well known to the general public for the equation E=mc², which establishes an equivalence between the mass and energy of a system.








 Informar de un error
Informar de un error Imprimir la página
Imprimir la página Comparte mi selección
Comparte mi selección Haz una pregunta
Haz una pregunta Consignar / vender
Consignar / vender
 Descriptivo
Descriptivo















